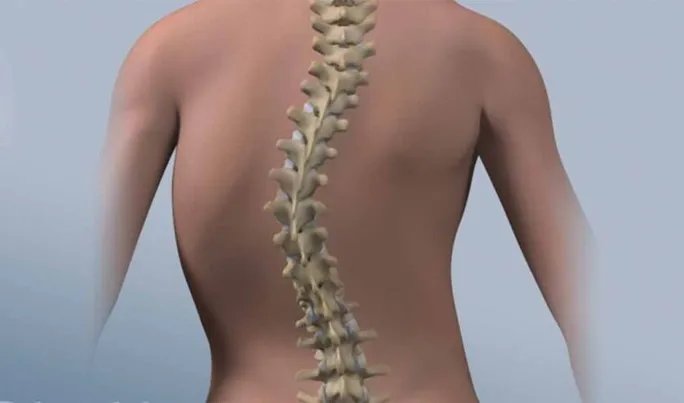
Here are some common deformity spine surgeries :
- Scoliosis : Scoliosis is a lateral (side-to-side) curvature of the spine. The spine may curve to the left or right, and it can be classified as congenital (present at birth), idiopathic (of unknown cause, often appearing during adolescence), or degenerative (developing later in life due to wear and tear on the spine).
- Kyphosis : Kyphosis is an excessive forward curvature of the spine, leading to a rounded or hunched back. While some degree of kyphosis is normal, excessive curvature can result from conditions such as Scheuermann's disease, osteoporosis, or congenital malformations.
- Lordosis : Lordosis is an exaggerated inward curvature of the spine, typically in the lumbar (lower back) or cervical (neck) regions. It can be caused by factors such as obesity, poor posture, muscle imbalances, or conditions like spondylolisthesis.
- Flatback Syndrome : Flatback syndrome is a condition where the normal curvature of the spine is reduced or flattened, causing an imbalance in the spine. This can lead to problems with posture, gait, and overall spinal alignment.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis : Scoliosis can also be associated with neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, where muscle weakness or imbalance contributes to spinal curvature.
- Adjacent Segment Disease : This is a degenerative condition that can occur after spinal fusion surgery. It involves the development of problems in the spinal segments adjacent to the fused area, leading to changes in curvature and alignment.
Treatment options for spinal deformities depend on the type and severity of the deformity, as well as the individual's age and overall health. Conservative treatments may include physical therapy, bracing, and pain management. In more severe cases or when conservative measures are ineffective, surgery may be considered. It's essential for individuals with spinal deformities to consult with orthopedic specialists or spine surgeons for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. The choice of treatment will depend on the specific characteristics of the deformity and the individual's overall health and lifestyle.