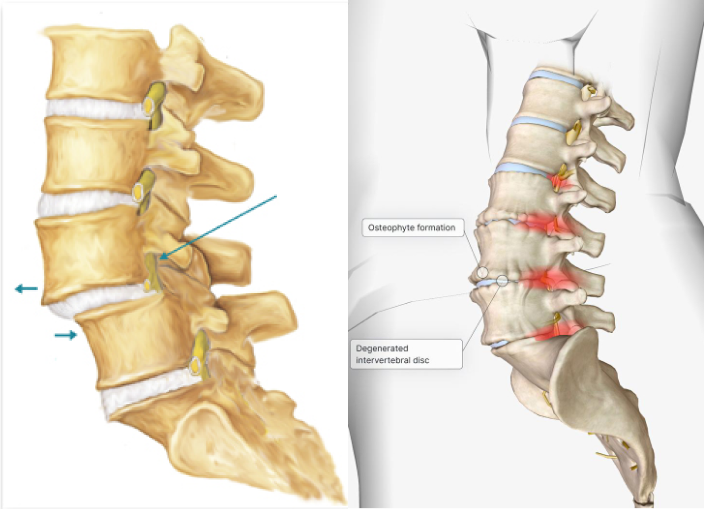
Here are some common degenerative spine surgeries :
- Discectomy : In cases of degenerative disc disease or disc herniation, a discectomy may be performed. This involves removing a portion of or the entire intervertebral disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
- Spinal Fusion : Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that involves joining two or more vertebrae together to eliminate motion between them. It is often used to stabilize the spine in cases of instability, such as spondylolisthesis or after a discectomy.
- Laminectomy : A laminectomy involves removing the lamina, the back part of the vertebra, to create more space within the spinal canal. This procedure is often done to treat spinal stenosis, a condition where the spinal canal narrows and puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
- Foraminotomy : In cases of nerve root compression due to bone spurs or other structures narrowing the neural foramina (the openings through which spinal nerves exit the spinal canal), a foraminotomy may be performed to enlarge the foramina and relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Artificial Disc Replacement : Instead of fusing the vertebrae together, artificial disc replacement involves removing a damaged intervertebral disc and replacing it with an artificial disc. This procedure aims to maintain spinal motion while addressing disc-related issues.
- Facet Joint Surgery : Facet joints can degenerate and cause pain. Surgical procedures such as facet joint denervation or fusion may be considered to address facet joint-related problems.
It's important to note that surgery is usually considered after conservative treatments have been exhausted, and the decision to proceed with surgery depends on the specific diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and the patient's overall health. Each surgical option has its own risks and benefits, and the choice of procedure should be tailored to the individual patient's needs. As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with degenerative spine surgery, and patients should thoroughly discuss these with their healthcare provider. The decision to undergo surgery should be made in collaboration with a qualified healthcare professional based on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's condition.